Major Considerations include:
4.1 Tangible Input
4.2 Output
4.3 Input-Output Technology
4.1 Tangible Input:
Tangible input presents the input modalities used to interact with information.
• “What kind of medium is used for input? What kind of interface we use to interact with information?”
There are wide range of possibilities to decide the input modalities depending on the content and context. For example, placing a product introduction card on the surface must provide information about the product or placing a cube on the table surface.
E.g. Wall, table, document, 3D objects.

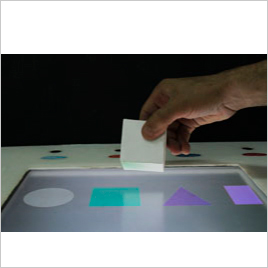
4.2 Output:
Output represents the output possibilities used to provide information/ required data to users.
• “What kind of a medium is used for output? How the information is been showcased?”
There are several possibilities to decide the output medium to showcase information to users. The output may range from a desktop screen to wall-projected surface to audio output and mechanical movement of 3D objects.


4.3 Input-Output Technology:
Input-Output technology represents the importance of technology understanding and usage in tangible user interface.
• What is the technology behind the input-output interactions?
• “What kind of possible input technologies are available today?”
Understanding of technology plays a vital role in defining interaction modalities. Designer needs to be aware of latest possible technologies, their functionality & possible usage is designing application.
E.g. Use of QR code in advertising. Due to technological advancement, the technological components have become smaller, cheaper & smarter to use. Also, development of tools such as arduino, RFID phidgets etc. and software such as reactivision, processing, vvvv etc. have made hardware prototyping much easier.
Technologies such as different kinds of sensors, camera, barcode, image processing, 2D pointing, audio capture, speech recognition, actuators etc. can be used for TUIs.
(Image: arduino, processing, fiducial).