Adhesives for plastics are a chemical compound that adheres to the mating surfaces of the plastic and cure to form the bond. Adhesives are capable of joining plastics with other plastics, metal, rubber, ceramic, glass wood etc. This technique produces permanent bond. Curing time is the most important factor for selecting an adhesive.
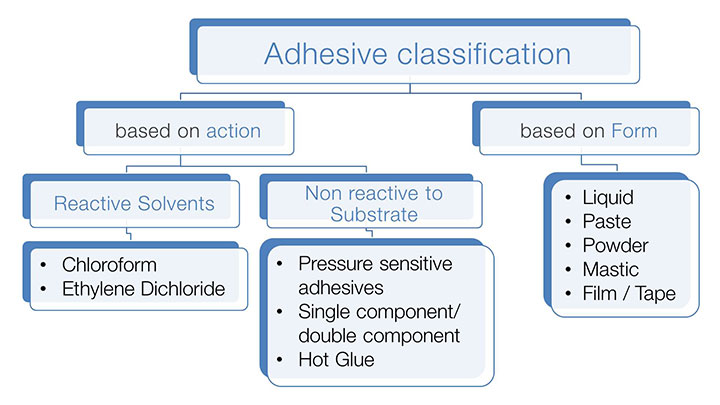
Adhesives are classified broadly based on the action and on their physical form. Based on action adhesives are classified as reactive solvents such as chloroform, ethylene dichloride etc. and non-reactive to substrate like pressure sensitive adhesives, single component/double component adhesives and hot glue. Based on form adhesives are classified as liquid, paste, powder, mastic and film/Tape.
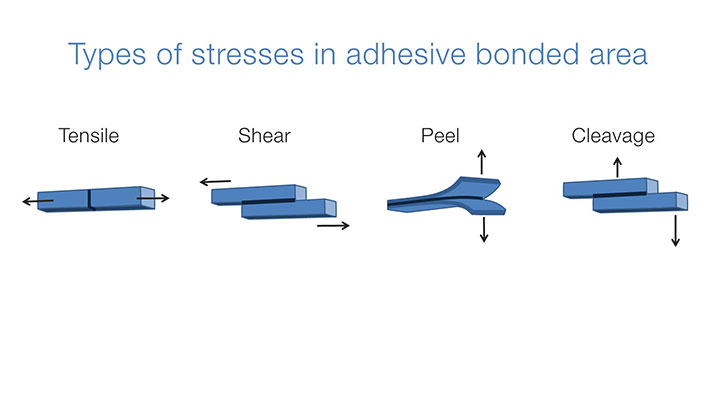
All the plastic components are subjected to the stresses during their service time. Based on the direction of application of force the types of stresses existing in adhesive bonded areas are tensile, shear, peel and cleavage.
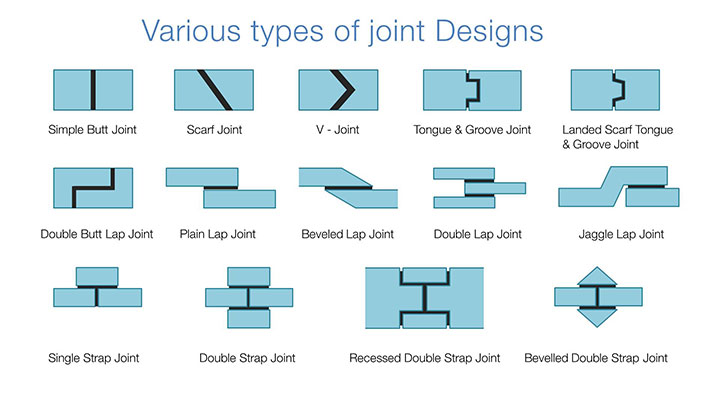
Adhesive joints are stronger in shear and tension than in peel and cleavage. Therefore a joint must be designed to sustain load in a way that utilizes their strength. For designing the joints for maximum strength the shear area is maximized so that shear force gets distributed over a large area and shear stress gets reduced.

