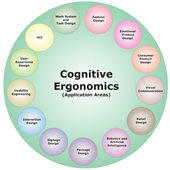
‘Cognition’ is the set of mental process which takes place between sensation, perception (awareness of sensation and pattern recognition) and the response (output). In other words, cognition is the mental process underlying our ability to perceive the world, remember, talk about and learn from our experiences, and modify our behavior accordingly. Therefore, each cognitive process is used to transform, reduce, elaborate, store, recover and use of sensory input (Bailey, 1996). The concept and meanings of cognition may be stated from perspectives:
- Understanding about objects/ events/ surrounding environment
- Perception and consequent acceptance of meaning of objects
- Thought/ Thinking process
- Reasoning and interpretation
- Initiator of emotion(s)
Reason (1988) summarizes four important traits of cognitive process: cognitive control modes, a restrictive workplace, automatic processors and activation.
Cognitive control modes- Cognitive processing is separated into conscious/unconscious modes and cognitive activity which is guided by their interplay. Conscious attentional control is typified as ‘serial, slow, laborious, resource-limited, analytic and computationally powerful, processes accessible to consciousness, essential for coping with novelty (newness) and cannot be sustained for any length of time.’ On contrary, unconscious controls are ‘parallel, rapid, effortless, no apparent limitations, intuitive, operated by simple heuristics, process beyond the reach of awareness (only products available to consciousness), capable of handling routines and recurrences but often ineffective in the face of change.’
A restricted workplace- In this trait, ‘attentional processing in within a short term memory/ working memory upon five to six discrete informational elements to identify goals, choose means to achieve them, monitor progress toward them and detect and recover from errors.’
Automatic processors- ‘A processor is the recollection of what has worked successfully in the past.’ It serves as expert knowledge structures that can be employed when there is a need in response to specific triggered condition. The knowledge structures are generally stored in a long-term knowledge base (long-term memory) and control the bulk of cognitive activity.
Activation- Most of the researches thought that processors can be activated by more than one influential cause which includes frequent and current employment of signals, features shared with other knowledge structures and emotional factors.