Formal Aspects
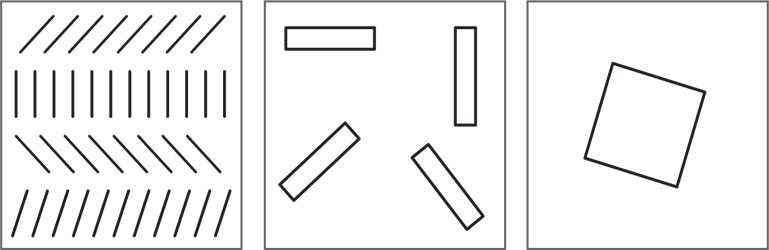
Orientation refers to the direction of the elements or the representation.
Orientation of an element depends on how it is related to the observer, to the frame of reference or to the other elements in the field.

Orientation is a relative factor. We can say that an object/representation has a particular orientation only in relation to another.
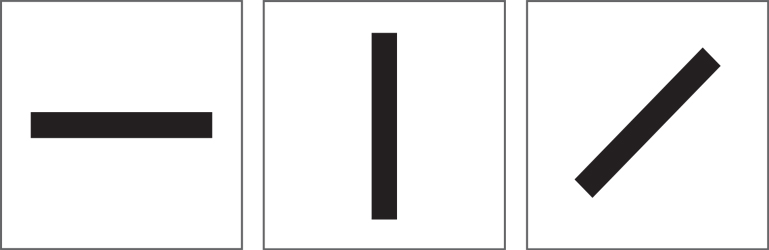
The primary directions are horizontal, vertical and the diagonal.




Semantic Aspects
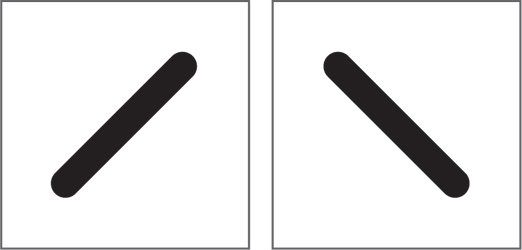
Orientation of an element or object can give rise to a strong sense of movement or dynamism, especially along the diagonal direction. Compared to this, the vertical and horizontal direction represents a sense of balance, stability and calmness.
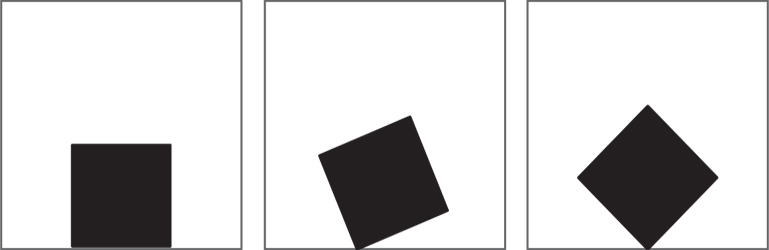
A horizontally placed square that looks static, on changing its direction along the diagonal axis, becomes dynamic.
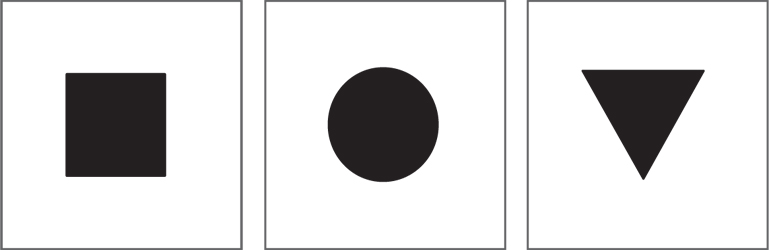
Square: denotes stability
Circle: denotes unity and wholeness
Triangle: denotes dynamism and conflict
Practical Aspects

Orientation indicates the direction of an object or representation.
Direction is useful for aligning different elements or objects in a frame of reference.

