Generally, harvested rattan is processed immediately, depending upon the type of rattan number of treatment is applied to transfer raw rattan into processed rattan. Processing of rattan helps in improving the quality of the rattan which helps in the product making minimizing the loose of time and money. There are two method of processing rattan.
Traditional Method:
Generally, harvester wear long trousers, long-sleeved shirt and plastic boots to avoid spines which are present on the surface of rattan, as soon as rattan arrives to the workshop/work area, the outer skin is scraped off with help of blade. Rattan is now allowed to dry for about seven days, which helps in reducing the water content. Removing the moisture from rattan helps in preserving it for about one and half months. Large diameter dried rattan can be used for making the frame of the furniture and the small size rattan are used for binding and weaving the frame.
Modern Method:
Many consider modern method are more costly and highly toxic, hence the people involved use face mask and pair of certified gloves. Diesel oil is filled in the curing tank
Although more expensive, this method produces higher quality products. In addition to the tools required in the traditional method, it is also necessary to have two chains, a curing tank, face masks and a pair of gloves. Metal chain is wrapped around the rattan bundle and it is dipped in the hot boiling oil. The oil treatment completely depends upon the type of rattan and time of harvest. Freshly harvested rattan is given 30 minutes of treatment and 3 days before harvest rattan is given 20 minutes of treatment. This treatment helps preserving rattan from 1 to 6 months. This treatment helps to remove larva and insect from the rattan, addition to that it brightens the color of rattan. It is important not to boil oil more than 100 degree centigrade otherwise the oil may catch fire.
Rattan is placed upright for 12-16 days, the dried rattan are inspected for any defects and defected pieces are rejected on the spot, large size rattan undergoes the transformation process after they have been scrapped. The small size rattan are scared and used in the weaving or binding process.
Weaving or Binding:
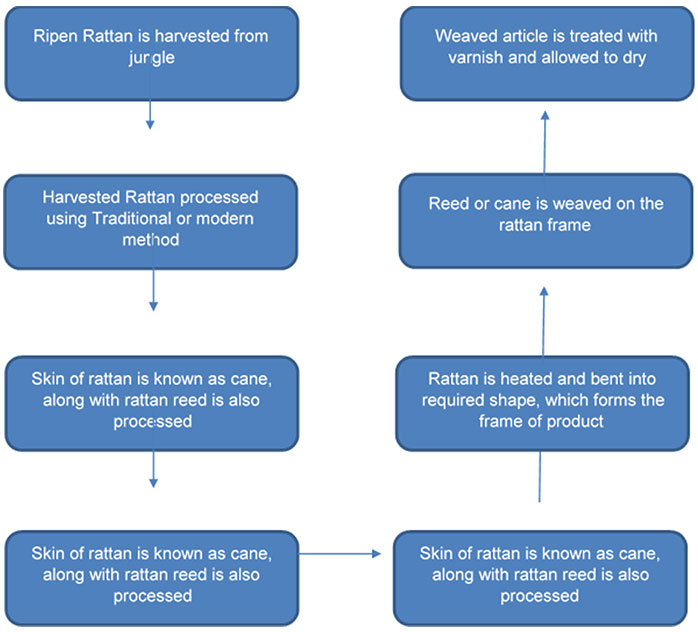
There are literally 1000’s of pattern and style of weaving a natural fiber basket and products. Weaving style is not only limited to an individual but also it can also tell us a lot about its place of origin. Style and pattern also depends up on the type of raw material chosen by the artisan. Some of the commonly found weaving styles are: - coiling, plait coiling, plaiting, multi-directional plaiting and twining.
Coiling: When a single or bunch of rods of natural fiber (like Reed or cane) are made into coils, the process is known as rod coiling. Generally coiling pattern weaving starts with spiral coiling. As the weaving progress, each turn in secured with previous turn by binding them. When materials like rattan is used, it is nailed to the previous coil when making large size basket. The interlocking between the stitches may or may not happen, which is depended weaver. Same technique can be to weave vertically. Using this technique shape like cylinder, cone and jar can be made.
Plait coiling: It is one of the simplest form of weaving products, it involves places of two set of strips vertically but slighting towards 60 degree angle and other set of strap interlacing them , so that each strap pass over one and under one, this process is continued still the required weaving pattern or result is obtained. Twilling can be done using the same technique, where one strip passes through more than 2 strips.
Multi-directional plaiting: Multi-directional plaiting is similar to the above mentioned process, the main difference is the implementation of the technique, multi- directional plaiting can be generally seen on the sitting chairs. The process is carried out on a chair frame with holes, these holes are made so that the strips can be passed through them. Artisan use three or more strips which are plaited in different direction. Once the weaving is completed, hole can be seen in the pattern which are hexagonal or octagonal depending upon the number of strips used.
Twining: This technique generally requires two set of elements. Generally, both the elements are the same materials. One element act as a passive and other act as an active element. In some of the product passive element could be the frame of product. Passive element is considered as wrap and active as weft, weft elements work as a pair. One weft strip passes below the passive element and other pass over it. They are twisted which helps them swapping over, nails are also used to strip permanently.
Artisan introduce heat to material like rattan and bamboo, which helps in shaping, these material are generally used as a main frame of the product to be made. The burnt outer layer of the frame is removed with the help of Sharpe blade. An artisan can use a single or all the technique to weave the required item. Depending upon the product to be made and availability of the raw materials.
Some of the most commonly used pattern are:-
 |
Circular weaving |  |
Rectangular weaving |
 |
Cross weaving |  |
Spiral weaving |
 |
Hexagonal Weaving |  |
Square Weaving |
 |
Twisted Weaving |  |
V-shape Weaving |
Flow chart: