Light since Antiquity:
Light has been fascinating mankind since antiquity through their various shades and colors. All of us see light every moment and everywhere but physicists peeped “into” these valuable gifts of nature to fathom what they are. The curious insights into these enigmas led to the development of most important branch viz., optics.
The Greeks believed that light sources emit tiny particles that stimulate vision upon entering the eye. In the 18th century several physicists, including Newton, studied light. Newton proposed the corpuscular (particle) theory of light. However, these models failed as they lacked agreement with the experiment.
Later Huygens proposed the wave theory of light that was highly successful due to its close agreement with experiments. Maxwell found the speed of light using the theory of electromagnetism that was in nice agreement with the experimental value measured by Fizeau. Coincidence of these two numbers is considered a major milestone in the history of physics. we can see only a very narrow range of the electromagnetic spectrum from 4000 A to 7000 A (A means angstrom, the unit of wavelength equivalent to 100 millionth part of a centimeter).
Light:
1. Light Emitting Diode
2. Working of Light Emitting Diode
3. Contribution of Art and Design using LED technologies
1. Light Emitting Diode:
• History:
For the past 150 years, lighting technology was mainly limited to incandescence and fluorescence. While derivative technologies such as high-intensity discharge lamps (HID) have emerged, none has achieved energy efficacies exceeding 200 lm/W (for monochromatic low pressure sodium lamps), with of less than 28 lm/W. With the advent of commercial LEDs in the 1960s, however, a new kind of lighting became available.
LEDs can consume less electricity than conventional lighting and can produce less of the parasitic by-product heat. However, at present, commercial LED systems are not as efficient as fluorescent lighting. Initial LEDs were red in color, with yellow and orange variants following soon thereafter. To produce a white SSL device, however, a blue LED was needed, which was later discovered through materials science and extensive research and development.
Light emitting Diode_(Image source)
In 1993, Shuji Nakamura of Nichia Chemical Industries came up with a blue LED using gallium nitride (GaN). With this invention, it was now possible to create white light by combining the light of separate LEDs (red, green, and blue), or by placing a blue LED within a special package with an internal light conversion phosphor – some of the blue output becomes red and green with the result that the LED light emission appears white to the human eye.
2. Working of Light Emitting Diode:
LEDs differ from traditional light sources in the way they produce light An LED, is a semiconductor diode. It consists of a chip of semiconducting material treated to create a structure called a p-n (positive-negative) junction. When connected to a power source, current flows from the p-side or anode to the n-side, or cathode, but not in the reverse direction. Charge- carriers (electrons and electron holes) flow into the junction from electrodes. When an electron meets a hole, it falls into a lower energy level, and releases energy in the form of a photon (light). The specific wavelength or color emitted by the LED depends on the materials used to make the diode.
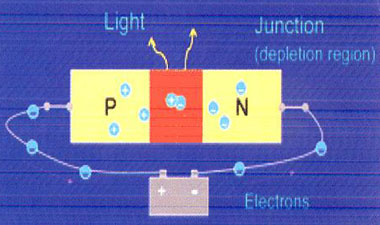
Working of LED.
• Future of LEDs: OLED:
OLED or organic light emitting diode is another technology creating ripples in the industries. Its making revolutions in revolution in laptop screens, mobiles and PDA. Its main advantages are that it draws less power, thinner and lighter than LCD, better contrast than LCD and it does not need backlight to function.
3. Contribution of Art and Design using LED technologies:
I also went through some of the latest design innovations in the field of Light Emitting Diode technologies.

Contribution of art and design in LED technologies.

