Inherent proportions involve the direct correlations of one element part to another.
For example:
The measurement of the length and width of a plane determine the exact length of the lines that border it. If proportions of the plane are changed then the length of the lines will be altered in correspondence to the plane.
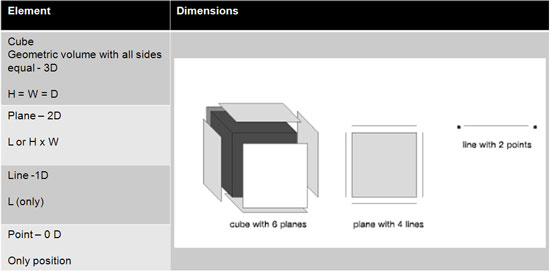
A cube comprises of the elemental parts planes, lines and points to limit its total mass and to delineate and punctuate the transitions between surfaces. All six planes on the cube are identical in size and all the lines on the plane are therefore the same length.
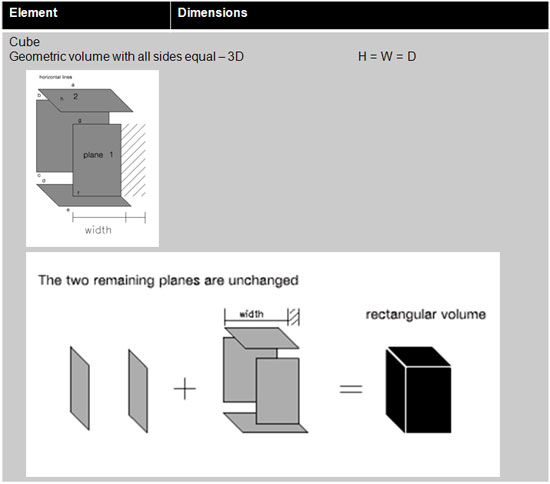
Inherent proportions involve the direct correlations of one element part to another
The change in the width of one plane directly affects the proportions of three planes including its edges(lines) as well as the relative inherent proportions of the entire volume.