Since the advancements in technology built the various styles and approaches to illustration, the story of how illustration grew in India also can be traced back to these advancements.
• 9000 BCE
The earliest illustrative drawings to be found in India go back to Bhimbetka Cave Paintings. Cave walls and stones being the favoured surface and paint used with hands representing basic forms from nature became the very first example of ‘illustration’ in India.
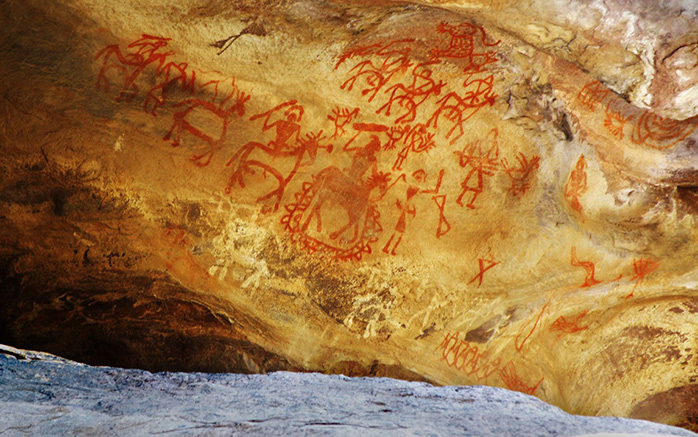

Cave Paintings of Bhimbetka. (Image source)
• 3300 BCE
Indus Valley Civilisation emerging in the northwest part of India developed into the first organised settlement. This period saw the development of art, economics, language and architecture all of which had to be documented and recorded. Thus the Indus Valley script was developed. These symbols in the form of seals were applied in many ways, including carving, chiselling, painting and embossing and the seals themselves were also made of many different materials, such as soapstone, bone, shell, terracotta, sandstone, copper, silver and gold.

Indus Valley Seals. (Image source)
• 2500 BCE
Pots and clay were a popular choice to decorate with illustrations in the Indus Valley Civilisation. Red based pots were painted over by black paint to add further graphics on the pots for decorative purposes only. Red pottery with red and black slip-painted decoration - Indus Valley.

Red Pottery from Indus Valley. (Image source)
• 2600-2000 BCE
Metals like gold, silver, brass, bronze, iron and tin, copper were used as printing materials too, incised with mirrored images and text.

Metal stamps from Indus Valley. (Image source)
• 15th to 6th century BCE
In southern India, palm leaves tada or tala or tali were widely used for writing manuscripts. Rig Veda itself contains many illustrations accompanying the texts, handwritten on birch bark or palm leaves.

Vedic Illustrations. (Image source)
• 5th century BCE
Buddhism not only urges the devout to hear, learn, remember and study the text but to obtain a good copy and to preserve it. This ‘cult of the book’ led to techniques for reproducing texts in great numbers, especially the short prayers or charms known as dharanis. Stamps were carved for printing these prayers on clay tablets from at least the seventh century, the date of the oldest surviving examples.
• 3rd century BCE
Ashokan Pillars were used by emperor Ashoka for Buddhist documentation and spread of religion. Pillars and temple walls depict the life of Ashoka.

Wheel of Law at Sanchi. (Image source)
• 2nd century BCE to 1st Century CE
Ajanta Frescos was created during the Satvahana empire on cave walls.
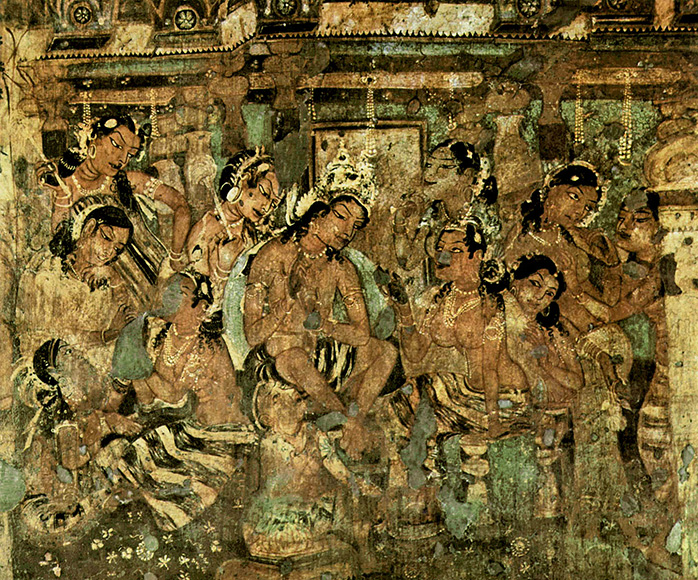

Wall paintings from Ajanta Caves. (Image source)
• 3rd Century
During the Gupta Period art and craft in north India reached its peak. Textiles woodblock printing on textiles emerged as a major craft. Wooden blocks were also used for writing.
• 6th to 7th Century
Chalukyas Art craft reaches its zenith and temple architecture flourishes.

Badami cave temples. (Image source)
• 7th Century
During this time literature in various parts of India exploded. Paper, invented in China was introduced to India in 7th century by Chinese prisoners from Samarkand but was not in popular use. During this time The Palas of Bengal pioneered miniature paintings.
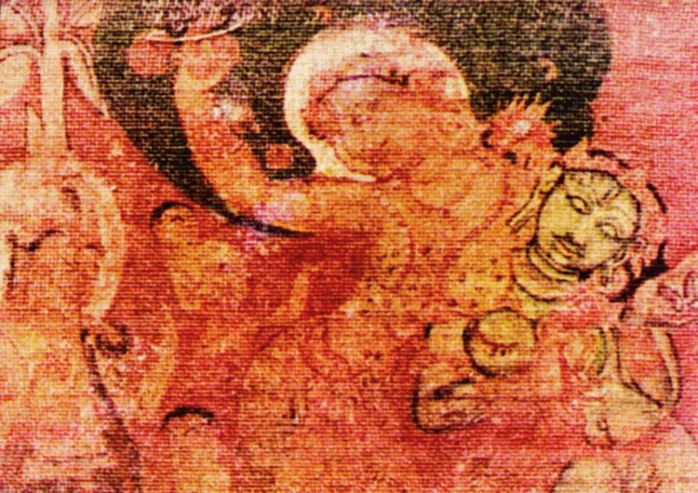
Astasahasrika-prajnaparamita, Mahipala era, c. 983 A.D. (Image source)
• 9th to 13th Century
Coins and temples are illustrated with the life of the Cholas. Scenes from Ramayanam Mahabharatam, Puranas and lives of the 63 Nayanmars are sculptured in narrative panels. The Cholas excelled in the art of portrait making. The best specimens of portraits are found on the walls of various temples from the Chola dynasty.

Coins of Chola Empire. (Image source)
• 12th to 16th Century
During the Mughal Period of Turks and Mongols, Akbar nama/Ain-i-Akbari, A chronicle of Emperor Akbar is commissioned by Akbar Himself and written by Abul Fazl. At least 49 different artists contributed to illustrating the stories in the form of Mughal miniature paintings. Apart from Painting on paper and Architecture, Mughals also patronise ‘Kalamkari’, an art form of illustrating on textiles.
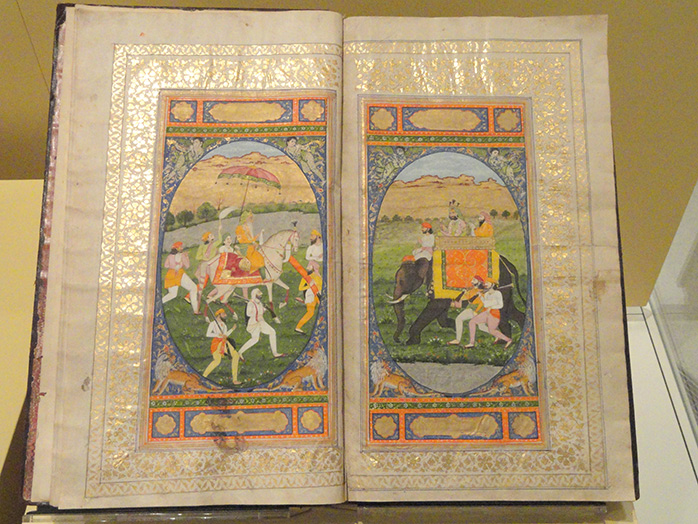

Source: Wikimedia Commons
• 16th Century
The first printing press in India reached Goa, in 1556, from Portugal. In 1568, the first illustrated cover page (the illustration being done with the relief technique of woodblock) was printed in Goa for the book ‘Constituciones Do Arcebispado De Goa’.
• 1706 - Bartholomaeus Ziegenbalg, a Danish missionary, arrived at Tharangambadi and printing in India could flourish again.
• 17th Century
During the East India period, Chamba Rumal craft originated, developed and flourished in the erstwhile state of Chamba.

Chamba Rumal depicting the life of Krishna. (Image source)
• 18th Century
The Hastividyārnava, an illustrated manuscript of Assam was written by Sukumar Barkaith, commissioned under the patronage of King Siva Singha and his queen consort Phuleswari. The manuscript deals with the management and care of elephants in the royal stables.

Hastividyarnava, Illustrated manuscript of Assam. (Image source)
Oriental scenery by William and Thomas Daniell (1769-1837), printed in monochrome and individually stained in coloured ink became the first example of single sheet printing on a large scale in India. The first magazines were published by the British. The earliest to appear was the Oriental Magazine; or, Calcutta Amusement (1785–86).

Oriental scenery by William and Thomas Daniell. (Image source)
• 1816 - The first printed illustrations of engravings by an Indian artist were by Ramachand Roy for the book Annadamangal. Published by Ganga Kishore Bhattacheryee, a journalist, teacher and reformer, it was printed at the Ferris and Company press of Calcutta.

Annadamangal illustration. (Image source)
• 1822 - Credit for the first single sheet lithographic print goes to the French artist De Savignac. He made a lithographic reproduction of a portrait of Warren Hastings, first Governor-General of Bengal, after an original painting by George Chinnery.
• 1824 - The Government Lithographic Press was established in Calcutta in 1824 leading to the printing and publishing of lithographic illustrations.
• 1850 - The Madras School of Art is established in Madras

Government College of Fine Arts, initially known as the Madras School of Art. (Image source)
• 1854 - School of Industrial Arts in Calcutta is founded.
• 1861 - The Archaeological Survey of India was founded, leading to extensive documentation of Indian subcontinent in the form of detailed maps and illustrations of heritage sites of India.
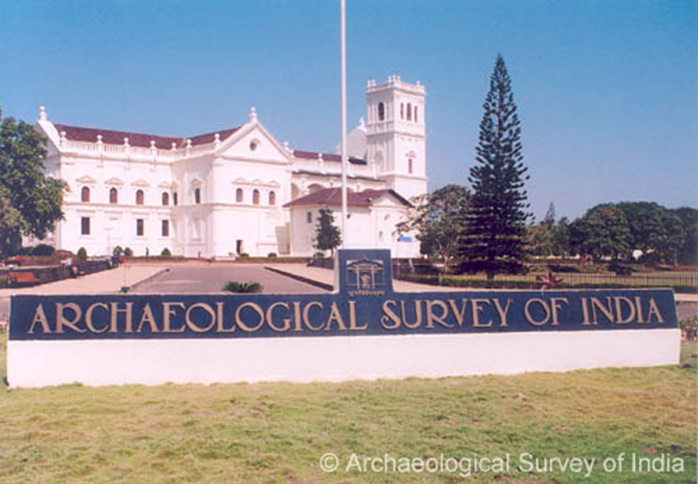

Churches of Old Goa. (Image source)
• 1866 - Sir J.J. School of Arts, is founded in Mumbai.

Sir J.J. School of Arts. (Image source)
• 1866 - Jeypore School of Industrial Art, is established in Jaipur.

Blue Pottery from Jaipur school of Art. (Image source)
• 1875 - Mayo School of Art established in Lahore.
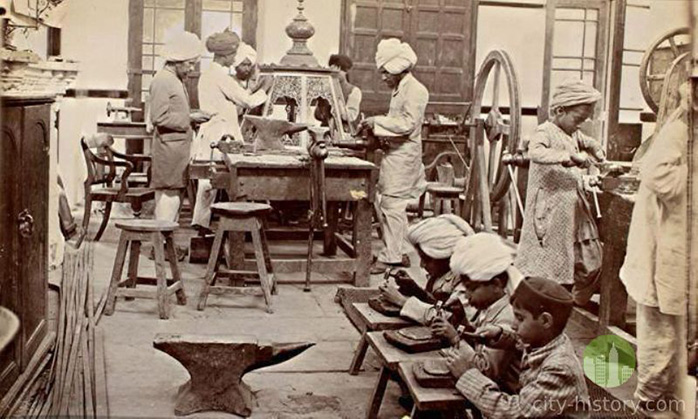

Mayo School of Art. (Image source)
• 1880 - The Illustrated Weekly of India starts publication.

The Illustrated Weekly of India. (Image source)
• 1895 - Upendrakishore first introduced modern block making, including half-tone and colour block making, in South Asia. When the reproduction using woodcut line blocks of his illustrations for one of his books, "Chheleder Ramayan" were very poor, he imported books, chemicals and equipment from Britain to learn the technology of block making. After mastering this, in 1895 he successfully set up a business of making blocks.

Illustrations from the book Chheleder Ramayan. (Image source)
• 1899 - The oleographic prints of Raja Ravi Varma published from his lithographic press at Lonavala in Maharashtra.

Arjun Subhadra by Raja Ravi Varma. (Image source)
• 1905 - Dattaram & Co, oldest existing Indian agency in Girgaum in Bombay.

Print ad by Dattaram & Co. (Image source)
• 1905 - Swadeshi Movement gaining momentum, rejection of ‘company style’ art.

Buy Swadeshi Ad Campaign. (Image source)
• 1907 - Indian Society of Oriental Art is founded by Abanindranath Tagore.
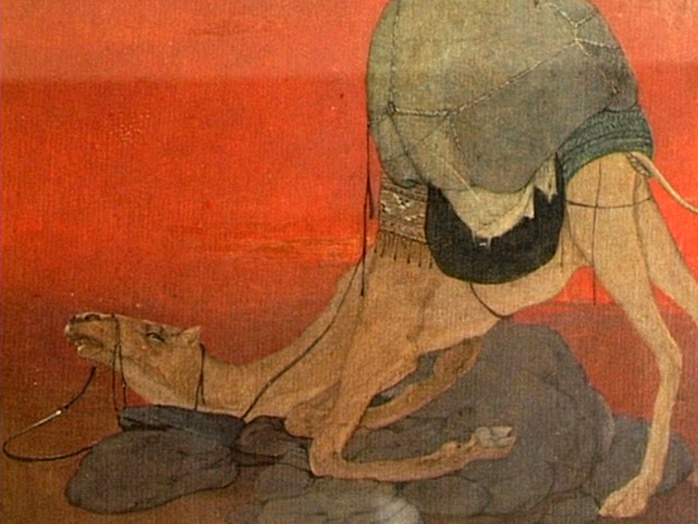

Journey’s End,1913 by Abanindranath Tagore. (Image source)
• 1907 - Bhartiya Bhandar Pustakalaya, was started in 1907 in Pakistan.
• 1910 - Sir J. J. College of Architecture founded in Mumbai.

Sir J. J. College of Architecture. (Image source)
• 1916 - Banaras Hindu University, established in Varanasi.

Banaras Hindu University. (Image source)
• 1919 - The Nobel laureate Rabindranath Tagore established a school of art in Santiniketan called Kala Bhawan.

Kala Bhavan. (Image source)
• 1924 - Statesman Weekly, an illustrated magazine of Indian news and views begins publishing.
• 1926 - Balak Magazine Published by Acharya Ramlochan Saran.
• 1932 - Mathrubhumi Illustrated Weekly, a malayalam magazine begins publishing in Kozhikode.

Mathrubhumi Illustrated Weekly, Logo. (Image source)
• 1936 - Rupa & Co. (Rupa Publications) was founded in Kolkata by D. Mehra
• 1942 - College of art

(Image source)
• 1942 - Indian Thought Publications is a publisher founded in 1942, in Mysore by R. K. Narayan.
• 1944 - K.C.S. Paniker founded the Progressive Painters' Association (PPA).
• 1946 - Air India's launches it’s mascot, the Maharajah (Emperor). It was created by Bobby Kooka, the then-commercial director of Air India, and Umesh Rao, an artist with J. Walter Thompson.

Air India Mascot. (Image source)
• 1947 - Chandamama, an illustrated children’s monthly magazine is published.
• 1949 - ‘Dharmyug’, a Hindi pictorial weekly is published.

Dharmyug Magazine cover. (Image source)
• 1950 - Bhartiya Bhandar Pustakalaya was re-established in India after partition as ‘Punjabi Pustak Bhandar’.
• 1952 - Post independence, a group of six artists - K. H. Ara, S. K. Bakre, H. A. Gade, M.F. Husain, S.H. Raza and Francis Souza, founded the Bombay Progressive Artists' Group.

Progressive Artists' Group. (Image source)
• 1952 - India Book House is formed in Mumbai.
• 1957 - Children’s Book Trust (CBT) is founded.

Book cover by CBT. (Image source)
• 1961 - National Council of Educational Research and Training (NCERT) educational books publisher is founded

NCERT Logo. (Image source)
• 1961 - Design Colleges like NID founded in 1961.

National Institute of Design. (Image source)
• 1967 - Amul India designs its mascot ‘Amul girl’.

Amul Girl. (Image source)
• 1967 - Amar Chitra Katha, a comic series was started by Anant Pai in Mumbai.

Amar Chitra Katha, Book cover. (Image source)
• 1969 - Industrial Design Centre is founded in IIT Bombay, Mumbai.
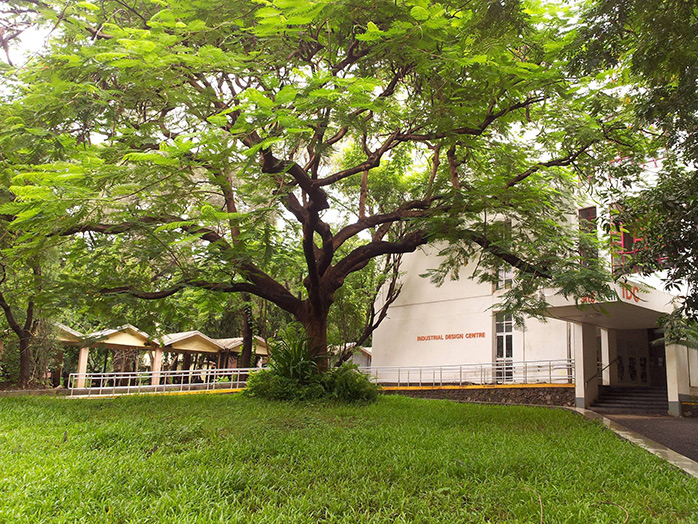

Industrial Design Centre, IIT Bombay. (Image source)
• 1969 - Champak, a children’s magazine is published by the Delhi Press Group. Lotpot, a Hindi comic magazine published by Mayapuri Group of publications also published.
• 1971- Cartoonist Pran Kumar Sharma, published the cartoon character Chacha Chaudhary for Lotpot magazine.

Chacha Chaudhary, illustrated by Pran. (Image source)
• 1974 - DC books, a publishing house is established in Kottayam, Kerala.
• 1978 - Diamond comics P Ltd. is established in New Delhi.

Diamond Comics. (Image source)
• 1980- Chitra Bharti Kathamala was a popular Indian comic book publication during the early 80’s.
• 1986 - Raja Pocket Books published in 1986 by Rajkumar Gupta. Later grew to become Raj comics.

Characters of Raj comics. (Image source)
• 1986 - National Institute of Fashion Technology is founded.

National Institute of Fashion Technology. (Image source)
• 1982 - Eklavya Foundation is an Indian NGO, setup in Madhya Pradesh. Eklavya aimed at reviving the Indian School Education system by developing the National Curriculum Framework.
• 1988 - Katha is a non-profit and non government organisation set up in New Delhi with the aim of community development, child welfare by education and literature. Founded by Geeta Dharmarajan.

CBSE recommended books by Katha. (Image source)
• 1984 - Mapin Publishing is an Indian art book publishing company started in Ahmedabad by Bipin Shah and Mallika Sarabhai.

Book Cover, Mapin Publishing. (Image source)
• 1984 - Urvashi Butalia and Ritu Menon set up India’s first feminist publishing house, Kali for Women.

Kali for Women, Logo. (Image source)
• 1990’s - Computers enter Indian Markets leading to blossoming of design firms and private design institutes as well as design departments in the industry owing to market liberalisation.
• 1994 - Orijit Sen published his illustrated novel, River of Stories, regarded as one of India’s first graphic novel.

River of Stories by Orijit Sen. (Image source)
• 1994 - Tara Books is an independent publishing house started by Gita Wolf in Chennai.
• 1996 - Tulika Publishers was founded as an independent publishing house by Radhika Menon. Based in Chennai, they published multi-lingual children’s books.

Tulika Publishers. (Image source)
• 2001 - Indian Institute of Cartoonists is founded in Bangalore.
• 2004 - Zubaan, a publishing house was formed headed by Urvashi, the co-founder of Kali for women.

Zubaan, Logo. (Image source)
• 2007 - Campfire Graphic Novels is set up in Delhi.

Graphic art by Campfire Graphic Novels. (Image source)
• 2008 - Indépendant illustrators emerge pan India with new forms of self illustrated publications.

Graphic Novels ‘Kari’ by Amruta Patil. (Image source)
• 2012 - Aadivani Publications, founded in Kolkata.
• 2012 - Abhishek Singh’s ‘Krishna- The Journey Within’ becomes the first Indian graphic novel to be published by Image Comics, an American publisher.
• 2014 - Penthrill Publication, founded in Kohima, Nagaland.
• 2014 - Kickstarter crowdfunded Graphic novel released called ‘Black Mumba’. Written by Ram V and featuring art by Devmalya Pramanik, Kishore Mohan, Rosh and Aditya Bidikar. Black Mumba is a collection of short stories revolving around life in Mumbai.

Cover, Black Mumba. (Image source)

