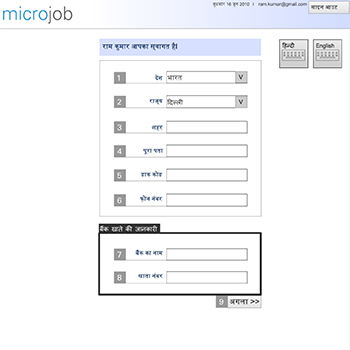
The micro-task market allows small tasks (typically requiring work for a few minutes or even seconds) to be posted as requests on a common web-based platform. These tasks are then distributed among large numbers of potential respondents. The respondent can select and complete any task for rewards that can be monetary or non-monetary (e.g., enhancing reputation). To ensure quality, the completed work is monitored through filters and peer review. One such micro-task service is Amazon’s Mechanical Turk. In this study, we investigated the barriers to such services being accessible to large numbers of potential users in developing country locations. For the purpose of comparative study, we adopted a few tasks from Amazon’s MTurk. The original MTurk interface was compared to four major interventions: MTurk in Kannada, Original UI and Kannada Video Instructions, Improved UI and Kannada Text Instructions, and Improved UI and Kannada Video Instructions. We calculated the effects of improved UI, instruction format, and language localization on the task completion and remuneration rates for micro-tasks among low-income novice computer users. We found that just language localization was not sufficient to enable micro-tasks, but improved UI and language localization proved positive. These results are instructive in outlining the challenges of having such supplementary income-generating opportunities benefit those with basic computer skills and low levels of income. We also present recommendations on key changes in the design of such services that can significantly impact access and usage among currently excluded user groups.