
105: Papermaking was invented by Cai Lun in China.

500: Early Arabic alphabet appeared. Although the historians disagree on both the birthplace and the birth date of Arabic writing, but it is widely accepted theory that it developed from Nabataean, which is one of the many West Aramaic dialects which served as the international language of the Middle East between the 4th century B.C. and the 7th century C.E.

570: Mohammed ibn Abdullah (570-632 CE), divine prophet of Islam was born in Mecca.

590 A.D.: Almost founded the Islam. Arabic script appeared in the Arabian Peninsula. The Kufic and Naskh styles were the first to be used by the ancient Arabs. For inscriptions on stones, Kufic script proved to be at once the easiest to incise and was the most majestic in appearance. The impressive style was carried over to record sacred works on parchment.

622 Hijra (flight of the Prophet Muhammad from Mecca to Medina): The beginning of Islamic era.

624: House of Muhammad in Medina was built. The main centre for prayer in the city of Medina was the Prophet's house. It was roughly square in plan, each side measuring some 56m, with nine small rooms along the East wall. Colonnades of palm trunks supporting palm branches were added along the North and the South walls as protection from the Sun, and the qibla orientation changed from Jerusalem to Mecca. This simple form had a lasting influence on the development of the Masjid in Islamic architecture.

642 – 650: Arab conquest of Persia (642: Azerbaijan, 649: Fars 650 Khurasan and 652 Merv).

651: The first Islamic coins were struck during the Caliphate of Uthman (644 to 656). These were the Persian dirhams that had an image of the Persian emperor Yazdgerd III with the addition of the Arabic sentence Bismillah (in the name of Allah). However, the first original minting of the Islamic dirham was done in 696-7 during Umayyad period.

656: Marked the murder of 'Uthman and beginning of the First Civil War in Islam; Ali ibn Abi Talib (600–661) reigned over Rashidun Caliphate. He was cousin and son-in-law of the Prophet Muhammad and the Fourth Caliph. Some Muslims believe he was the first Islamic Calligrapher.

661 saw decline of 'Ali Umayyad’s Dynasty (661–750), the first major ruling Muslim dynasty that was established in Damascus. Following the murder of Ali, power passed into the hands of Mu'awiya, the Governor of the province of Syria, a member of the powerful Banu Umayya family of Mecca, and a cousin of the murdered Caliph 'Uthman. He became the first Umayyad Caliph.
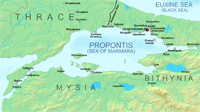
674-8 witnessed First Arab siege of Constantinople (former name of Istanbul, port city in northwest Turkey).

7th-8th centuries: The style of decoration on early Islamic metalwork is characterized by geometric and arabesque ornament, together with inscriptions in Kufic. Typically it is engraved, although some examples of inlaid decoration are also known. This silver ewer features engraved griffins and an eagle within ovoid medallions, niello geometric motifs, and gilding. It was made in Iran or Central Asia during the 7th or early 8th century.

691: Dome Rock Masjid in Jerusalem was built. Standing near the centre of the artificial platform known as the Haram al-Sharif ('the Noble Sanctuary'), the Dome of the Rock is the earliest Islamic monument to have survived in its original form to the present day. The form and decoration of the building are largely derived from Byzantine church architecture, and the ornament contains a number of motifs from Sasanid Iran. However, the inclusion of a Qur'anic inscription clearly identifies the building as Islamic. The earliest occurrence of Quranic calligraphic inscription can be found in the dome Rock Masjid.

7th century and early 8th century manuscripts were found in Hijazi script. The style of script used in Western Arabia during the first decades of Islam is known as Hijazi. The example shown here dates from the early 8th century.

705-14/15 Umayyad Masjid ('Great Mosque') in Damascus built at the order of the Caliph al-Walid I (705-15) at a time of political expansion. The Great Masjid of Damascus is a clear expression of the power and prestige of the Umayyads. The oldest part of the Masjid is the prominent and noteworthy square 45-meter minaret. The earliest restoration of the minarets dates to 1090, during the Seljuk dynasty. The minaret exhibits intricate bands of carved Kufic inscriptions along its length, that alternate with bands of stylized ornaments in patterns and muqarnas.

710 Arrival of Muslim armies in Spain. After sweeping across North Africa, Arab forces seiged Spain, led by Tariq ibn Ziyad (after whom Gibraltar-Jabal Tariq, or Mount Tariq - is named). The forces defeated the Visigoths, taking their capital Toledo in 712.

711 Arabs conquered of the Indian province of Sindh by Muhammad bin Qasim and brought their influence and coverage with them. Traces of early Islamic architecture on the subcontinent can be seen from the first half of the 8th century, at Hanbhore, East of Karachi, where foundations indicate a Masjid of Arab plan.

722 Arabic became the official language of the Khorasan and Transoxiana.

727: The art of Islamic calligraphy reached Indian subcontinent. The earliest wiring among the fourteen inscriptions discovered from the Muslim city of Banbhore is dated 109 A.H (727 CE) and 294 A.H. (906 CE) The Site of Banbhore (today the port Barbaricon) is located on the Northern Bank of Gharo Creek, 65 Kilometer East of Karachi, Pakistan.

750: Abbasid dynasty (750–969) established. It was the major Muslim dynasty that ruled in Baghdad. Ongoing rebellions in the vast and diverse territories conquered by the Umayyads finally led to the outbreak of a major revolt in Eastern Iran, which spread throughout the Islamic territories. The Umayyad dynasty was overthrown and power passed to Al-Abbas, a member of a rival family from Mecca, who descended from the Prophet's uncle. The Abbasid period saw the emergence of a full fledged Islamic style with its own distinctive repertoire of motifs; while at the same time philosophy, literature and theology thrived, and numerous works of science were translated from Greek into Arabic.

750: Around this year the animal fables known as Kalila wa- Dimna, of Sanskrit origin, known as Panchatantra, translated into Arabic from a Pahlavi source. During the 13th century, they were translated into Spanish, and a later French version was acknowledged as one of the sources of La Fontaine's fables.

751: Chinese defeated by Arab armies near Talas. Following this victory, the art of paper-making was introduced by Chinese prisoners of war. With learning of paper-making, the book-making and calligraphy were developed. Many of the surviving Arabic documents from the first three centuries of Islamic rule are on papyrus. Most of these are from Fustat, and record various aspects of daily life and administration.
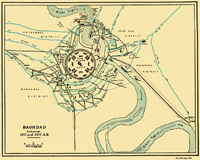
762 was the year of founding of Baghdad. In 762 the Caliph al-Mansur found a new capital, officially called Madinat al-Salam ('City of Peace'), better known as Baghdad. Al-Mansur's city was circular in plan with a diameter of some 2000m, and bisected by four main thoroughfares covered with barrel vaults. It was entered through elaborate two-storeyed gateways. Houses and shops formed an outer ring, while at the centre of the city were the palace and Masjid, and the Green Dome - a high dome, surmounted by a statue of a rider with a lance. Baghdad was the centre of Islamic calligraphy till late 13th century.

770: The first dated relief printing by Chinese.

784-5 (168 A.H.): one of the dated known copies of the Qur’an in Kufic. It is perhaps the one earliest and there are several others of the ninth century C.E.

784-6: Great Masjid of Cordoba was built in Spain. A large hypostyle hall with aisles running perpendicular to the qibla wall, the Great Masjid of Cordoba is the most important monument of Umayyad Spain. (Today it houses a Gothic cathedral at its centre.) There are splendour Kufic inscriptions in this Masjid.
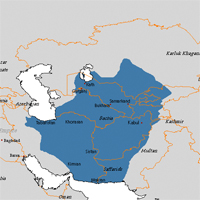
819: Samanid Dynasty (819-1005) founded. The Samanids, a Persian dynasty, are appointed as governors of Transoxania and Khurasan for the Abbasids. Their capital, Bukhara, is a brilliant cultural centre, associated with the flowering of Persian language and literature.

9th century: 'Blue Qur’an'. There are very few extant examples of Qur'ans dating before the 9th century. They are typically written on parchment, and the highly evolved Kufic scripts are sometimes accompanied by brilliant illumination in gold. The example shown, with its dyed pages, is from the celebrated 'Blue Qur'an'. It was copied in Tunisia or Spain in the 9th century.
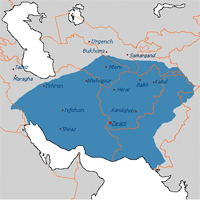
861 Saffarid Dynasty (861-1003) founded. The Saffarids are one of the first Iranian dynasties to challenge the rule of the Abbasids in Eastern Iran. They ruled in Sistan Southeast of Iran.
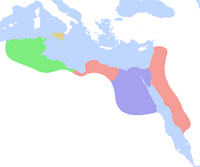
909 Fatimid Caliphate (909-1171, Cairo) founded. The Fatimid rulers in Cairo (founding in 969) proclaim themselves Caliphs in direct challenge to Abbasid power. They are Isma'ilis, an extreme branch of Shi'ism. The Fatimid Caliphate reached its peak during the reign of Al-Mustansir (1036-94), when its prosperity rivaled that of Baghdad.

940 July 20 Ibn Muqlah (Abu 'Ali Muhammad Ibn 'Ali Ibn Muqlah Shirazi) was murdered in Baqdad. He was an Islamic calligrapher, one of the foremost of the Abbasid age. Ibn Muqlah was an Iranian Origin vizier in ‘Abbasid court. He achieved great honour by completing the development of Kufic from its ancient forms into new forms, and his elegant new style was copied throughout Islamic calligraphy.

10th century slip-painted bowls from Nishapur and Samarqand; These slip-painted earthenware bowls from Nishapur typify the ceramic production of Eastern Iran during this period. The former from Nishapur were decorated with a superb band of calligraphy, the ascending strokes pointing inwards; the simple contrast between the white ground and the dark Kufic script which was highly effective. The Samarquand bowls were decorated with a seated figure.
970: Around this year the Seljuk Turks arrived to Islamic lands.
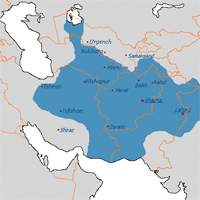
977 Ghaznavid Dynasty (977-1186). Power on the Eastern fringes of the Islamic world, in Central Asia and Afghanistan, gradually passes into the hands of local Turkic tribes, newly converted to Islam, who establish their own dynasties. The Ghaznavids are one of the first major Turkic dynasties. Their capitals were Ghazna and Lahore.

973 Birth of Abu Rayhan Biruni often known as Al-Biruni (d. 1048), perhaps the greatest intellectual figure of medieval Islam, in a village in southern Khwarazm. Alongside being a celebrated historian and geographer, Al-Biruni was also a highly accomplished physician, chemist, mathematician and astronomer. Following the Ghaznavid conquest of Khwarazm in 1007, Al-Biruni was taken to Ghazna, where he continued to write. Al-Biruni earned the "founder of Indology" and "first anthropologist" titles for his remarkable description of early 11th century India.

991 (381 AH.) Mahmud of Ghazni (r. 997-1030 C.E./387-421 A.H.) invaded Northern India. He vowed to raid India every year. Sultan Mahmud since 1001 C.E./392 A.H. till 1025 C.E./416 A.H., during 24 years, several times invaded different locations of India. He did that apparently for the intentions of Jihad with Indian infidels but he struggled to plunder their assets.

1000: Chinese Calligraphy printed perfection. In the East calligraphy has been consistently practiced as a major aesthetic expression. In China, from the 5th century B.C., when it was first used, calligraphy has always been considered equal, or even superior, to painting. Chinese calligraphy began with a simplified seal script, known as "chancery script," in which the width of the strokes varies and the edges and ends are sharp. The perfection of the brush in the 1st century made possible the stylization of chancery script into "regular script," distinguished by its straight strokes of varying width, and clear, sharp corners, and a cursive "running hand."
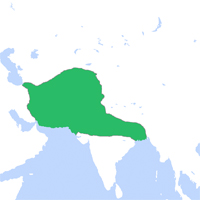
1000 Ghurid Dynasty (c. 1000 - 1215). The Ghurids, from the mountainous area of Afghanistan, southeast of Herat, extend their rule to include much of Khurasan, and raid deep into the Indian subcontinent, conquering Delhi in 1192.

1000: The early knitting from Egypt has Islamic calligraphy knit into it (mostly 'Allah', occasionally blessings).

