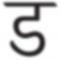Electronic devices mostly convey (display) information through the use of a display device. These display devices make use of certain display technologies such as LED (segmented) display, LCD, CRT displays etc. Each of these has a ‘display resolution’ which is the maximum number of distinct pixels (picture elements) that the device can display. A Pixel is the smallest screen element in a display. While representing raster images it is the smallest unit of a picture.
Raster images (such as photographs) are made up of millions of pixels, each having a specific colour and location. An important parameter that defines the pixel is its aspect ratio, which is the ratio of the width of the pixel to its height. It is important to note here that a pixel is not always a square (ratio 1:1); there are many rectangular pixels which have different ratios, such as 4:3 and 16:9.
Furthermore, it is also possible that pixels are not rectangular in nature. They can be circular and even capsule shaped. On a computer each pixel is a rectangle, but when displayed on a device they can be displayed through a series of circles, rectangles or capsules.
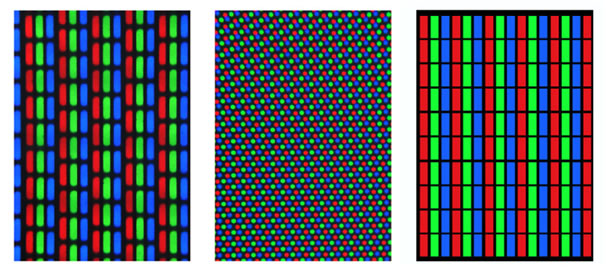
Figure 1: Pixels on a TV set, on a CRT Computer Monitor and LCD Monitor.
The above figure shows the different shapes of pixels that are seen in some common display devices.

Figure 2: Pixels on a Cathode Ray Tube Computer Monitor and the text displayed in it.
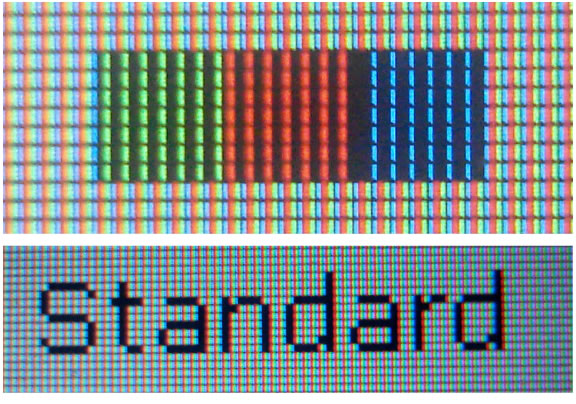
Figure 3: Pixels on a LCD Computer Monitor and the text displayed in it.
When text is fitted on to a grid of pixels, it might appear jagged. The jagged edges are called artifacts or the text is called aliased text (or edge). Smoothening these artifacts or removing aliasing from a text to make it look smoother and to make it blend properly with its background is called anti-aliasing.
In the figure given below, the letter on the left has jagged edges in comparison with the letter on the right which is anti-aliased.




Figure 4: Aliased letter (on the left) and anti-aliased letter (on the right).
Assignment 3:
• In the given assignment, please try and answer the following questions.
• Use the available books in your library, online sources or talk to experienced graphic/ type designers.
• After noting down the answers, please discuss your answers with your colleagues and faculty members.
There is a possibility that you might not reach a single unambiguous answer. The goal of the assignment is to stimulate a discussion rather than to come up with a definite answer. Some of the questions are purposefully challenging, complex and ambiguous in nature; they are meant for the more experienced students and faculty, but undergraduates should nonetheless attempt to answer them.
Q6. List down the various aspect ratios of pixels used today?
What are the different resolutions that are used in today’s devices?
Q7. What are the different shapes of pixels?
Why do different devices, have pixels of different shapes and sizes?
Q8. What are the methods used for smoothening fonts?
Find out and explain, “SubpixelRendering Optimization” technology.
Digital Typography Downloads:
• Presentation - Slideshow - pdf