Animation Principles - Arcs
Know more
Page 1 - What are arcs
Arcs refer to the natural, curved paths that most objects follow when they move. These arcs are important because they create more fluid and realistic motion, as opposed to stiff or mechanical movements. For example, when a character swings their arm or tosses a ball, the movement typically follows a gentle curve rather than a straight line. Using arcs helps to enhance the sense of weight, momentum, and realism in the animation
Principles of Animation - Arcs.
Arcs and How to Master Naturalistic Motion in Animation.
Page 2 - How it works
To create a swinging pendulum whose motion looks natural, you'd start by visualising the curved path the pendulum follows as it swings back and forth. Instead of placing keyframes in a straight line, you'd place them along this curved arc. As you adjust the curve in your animation software, you'll ensure that the pendulum swings smoothly, mimicking how it would move in real life. When you play back the animation, the pendulum should have a natural, fluid motion.
Page 3 - How it helps
Acrs help in creating a more natural looking motion, check this video out where Aron Blaise animates and explains with a demo how arcs work and helps in animation.
Animating with Arcs.
Page 4 - Arcs in dancing
Arcs are essential in animating dance movements because they capture the natural, curved paths of a dancer's body. Whether it's a twirl, an arm movement, or a step, these arcs make the dance look smooth, fluid, and realistic, reflecting the graceful flow of real-life dancing.
Page 5 - Arcs in Bowling
When a person throws a ball, the ball's movement follows an arc due to the forces of gravity and momentum. As the ball leaves the hand, it travels upward and forward, then curves downward as it loses speed and gravity pulls it back to the ground. In animation, replicating this arc is crucial to making the throw look natural and believable. By plotting the ball's trajectory along a curved path, you can capture the realistic motion of the throw
Page 9 - Arcs in running
Running involves more dynamic arcs, with longer, more exaggerated curves. The legs move in larger arcs as they propel the body forward, and the arms swing with more force and a broader range of motion, following wider arcs.
The body leans forward, creating a stronger downward arc as the runner's body moves up and down with each stride.
Page 10 - Arcs in walking
As a character walks, their limbs move in arcs. In this example, when a foot swings forward, it follows an arc before making contact with the ground. The arms also swing in arcs opposite to the legs, helping to balance the motion and create a smooth, rhythmic walk.
The head and torso have subtle arcs as they rise and fall slightly with each step, adding to the realism of the movement.
Page 11 - Arcs in swinging
Arcs are very much present when a kid is swinging on a swing. The swing itself moves in a large arc as it goes back and forth, following a curved path due to gravity and momentum. The kid's body also follows an arc, especially their legs as they kick forward or bend back. These arcs are key to capturing the natural, smooth motion of swinging, making the animation look realistic and fluid.
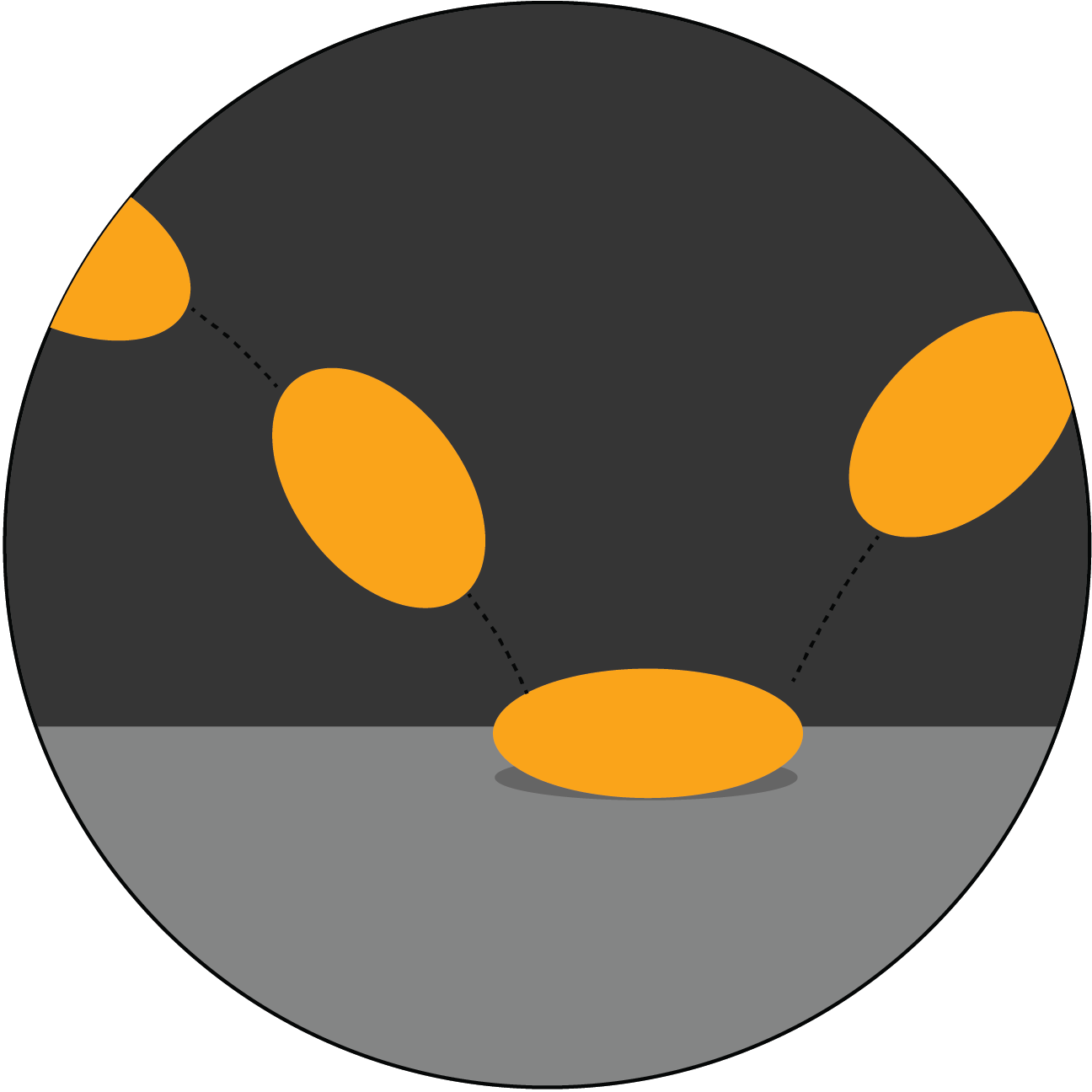
Page 12 - With vs without Arc
When arcs are present in animation, movements appear smooth, natural, and realistic, mimicking the way objects and people move in real life. For example, a character's arm swinging in an arc looks fluid and lifelike.
Without arcs, movements become stiff, mechanical, and unnatural. A straight-line motion, like an arm moving directly from point A to point B without an arc, looks awkward and robotic, breaking the illusion of reality in the animation.
Arcs are crucial for creating believable and visually pleasing motion, while the absence of arcs often results in unrealistic and jarring animation.