Interaction Design(IXD)
1891-1900
(1 items)
1991-2000
(3 items)
2000-2009
(1 items)
2000-2010
(3 items)
2001-2010
(5 items)
2011-2020
(18 items)
2020-2024
(1 items)
2021-2024
(3 items)
Interaction Design(IXD)
1891-1900
(1 items)
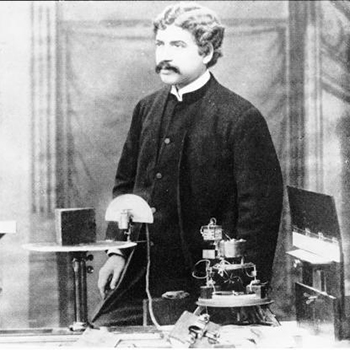
by Jagadis Chandra Bose
Jagadish Chandra Bose's demonstration of microwave communication at the Royal Institution in London in 1897 was a groundbreaking event in the history of wireless communication. Bose's experiments with electromagnetic waves laid the foundation for modern microwave technology and wireless communication systems. During his presentation, Bose used semiconductor diodes to generate and detect microwave signals. He used waveguides, horn antennas, dielectric lenses, various polarizers, and even semiconductors at frequencies as high as 60 GHz; much of his original equipment is still in existence, now at the Bose Institute in Calcutta. He demonstrated that these signals could be transmitted over short distances without the need for wires, showcasing the potential for wireless communication.
Bose's work was ahead of its time and contributed significantly to the development of wireless telegraphy and later radio communication. His experiments not only demonstrated the feasibility of microwave communication but also helped pave the way for the inventions of later scientists, including Guglielmo Marconi and Nikola Tesla, who further advanced wireless communication technology. Bose's contributions to science and technology are immense, and his experiments at the Royal Institution marked a significant milestone in the history of telecommunications.
1991-2000
(3 items)
by Prof. A.G. Rao & Prof. Ravi Poovaiah
The Electronic Voting Machine (EVM) is a reliable system for conducting elections in which one person has to be elected out of many candidates. The EVM is designed for single posts and single votes. In the 1980s, the Election Commission of India initiated efforts to modernize the voting process and reduce electoral fraud. Professor A.G. Rao, along with his team at the Indian Statistical Institute (ISI) in Kolkata, and later Professor Ravi Poovaiah, played crucial roles in designing and developing EVMs for use in Indian elections. Their work led to the creation of a reliable and tamper-proof electronic voting system that has been widely adopted in India. The EVMs developed by Professors Rao and Poovaiah's team have several security features to prevent tampering and ensure the integrity of the voting process. These include encryption techniques, secure storage of votes, and built-in mechanisms to detect any attempts at manipulation.
The introduction of EVMs has revolutionized the electoral process in India, making voting faster, more efficient, and less prone to fraud. EVMs have been used in multiple general elections and state assembly elections in India since their introduction, and they have generally been well-received for their effectiveness in streamlining the voting process and improving the accuracy of vote counting.
by Snehi NGO
by Pratham Education Foundation
2000-2009
(1 items)
by Sridhar Vembu and Tony Thomas
2000-2010
(3 items)
by Vijay Chandru, Swami Manohar, Ramesh Hariharan and V. Vinay
The Simputer, short for "Simple Inexpensive Multilingual People's Computer," was a pioneering initiative developed in India in the early 2000s by a team led by Vijay Chandru, Swami Manohar, Ramesh Hariharan, and V. Vinay. The concept behind the Simputer was to create an affordable computing device that could be used by people with limited access to technology, particularly in rural and remote areas. The goal was to bridge the digital divide by providing a simple, user-friendly device that could enable a wide range of applications, including education, healthcare, and commerce.
In terms of technological innovation, Simputer had an impressive list of firsts. It was the first Linux-operated handheld device with writing capabilities, the first handheld device to have a USB master port, and the first to have an accelerometer. Over 180 million students were in school, and only a lucky handful had just become familiar with computers. The digital divide was growing. In this backdrop, during the IT.Com event of October 1998, touted as the first large-scale IT expo in the country, the Bangalore Declaration on Information Technology for Developing Countries was released. One of the goals of this declaration was to make a Simple Inexpensive Mobile comPUTER (SIMPUTER) to provide access to information technology for every citizen, regardless of their social or economic status. This spurred four faculty members in the Department of Computer Science and Automation (CSA) at IISc – Vijay Chandru, Swami Manohar, Ramesh Hariharan, and V Vinay – to imagine and develop a low-cost handheld computer, one that could be accessible for everyone. Simputer was not the only innovation that came out of the partnership between the four. While Swami Manohar and V Vinay were setting up a company called PicoPeta to market the Simputer, Ramesh Hariharan and Vijay Chandru were also building a genomic company for personalised medicine called Strand Life Sciences.
by Prof. Ravi Poovaiah and Dr. Ajanta Sen
Jellow Communicator is an innovative communication tool designed to assist individuals with speech and language disabilities, particularly those with conditions such as cerebral palsy, autism, and developmental disabilities. The project was spearheaded by Professor Ravi Poovaiah and Dr. Ajanta Sen. The journey of Jellow started in 2004 as a tangible physical product. Following this, in 2008, it was made available on desktops. Then, after extensive user studies, it was conceived as a complete communication system available on a variety of platforms. Jellow has been supported by IIT Bombay, the e-kalpa project from the Ministry of Human Resources and Development, the Innovation Fund Award from Unicef, the National Trust, the Ministry of Social Justice and Empowerment, Nair Hospital, and the University of Connecticut, USA, along with several NGO's working in the field of persons with disabilities.
Jellow Communicator utilises a symbol-based communication system, making it accessible to individuals with limited verbal communication abilities. It consists of a grid of symbols representing various words, phrases, and actions. Users can customise the communication grids based on their specific needs and preferences. Grids can be tailored to different contexts, such as home, school, or community settings, and can include symbols related to daily activities, emotions, requests, and more. The use of symbols provides visual support to aid comprehension and expression for individuals who may struggle with traditional text-based communication methods. Jellow Communicator features voice output functionality, allowing users to select symbols and have them spoken aloud using synthesised speech. This feature enables users to communicate effectively with others, even if they are unable to speak verbally. The design of Jellow Communicator emphasises accessibility and ease of use, with intuitive navigation and user-friendly interfaces suitable for individuals of all ages and abilities. Jellow Communicator is available as a mobile application, making it convenient for users to access the tool on smartphones and tablets. The mobile app version offers portability and flexibility for use in various environments. Overall, Jellow Communicator is a valuable resource for individuals with speech and language disabilities, empowering them to communicate effectively and interact with others more independently. The project reflects a commitment to inclusive design and leveraging technology to improve the quality of life for people with disabilities.
by Nandan Nilekani
2001-2010
(5 items)
by Government of India
by Khabar Lahariya Team
by Saksham Trust
by Shaheen Mistri, Teach For India Fellowship
by Invention Labs
2011-2020
(18 items)
by DataWind
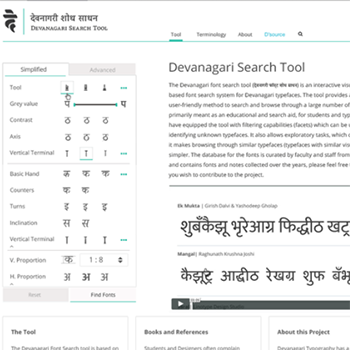
by Prof. Girish Dalvi and Yashodeep Gholap
"Ek Mukta" is a free and open-source Devanagari font designed by Professor Girish Dalvi and Yashodeep Gholap with extensive support from Noopur Datye, Sarang Kulkarni, and Maithili Shingre. It is a Unicode-compliant, versatile, contemporary, humanist, mono-linear typeface available in seven weights, supporting Devanagari and Latin scripts. This type family is a libre-licensed version of the Ek multi-script family, an ongoing project to develop a unified type family for each Indian script. The goal is to build one harmonious family across all Indian scripts without letting the visual features of one script dominate over others. This ensures that the fonts can be used successfully for both single and multi-script purposes.
Ek Mukta was designed with the aim of providing a contemporary and versatile Devanagari font that could be used for various purposes, including print and digital media. The font features a clean and elegant design, with balanced proportions and legible characters. It is released under the SIL Open Font License, which allows anyone to use, modify, and distribute the font freely. This open-source approach encourages collaboration and ensures that the font remains accessible to a wide range of users.
Professor Girish Dalvi, a renowned type designer and educator from IIT Bombay, collaborated with Yashodeep Gholap, a graphic designer and typographer, to create the Ek Mukta font. Their combined expertise in typography and design helped shape the development of the font and ensure its quality and usability. Ek Mukta supports not only Hindi and Marathi but also other languages that use the Devanagari script, such as Nepali and Sanskrit. This multi-language support makes the font versatile and suitable for a diverse range of applications. It has received recognition and praise for its design and contribution to the Devanagari typography community. It has been adopted by various organizations and projects for use in print publications, websites, and digital platforms. Overall, Ek Mukta represents a valuable addition to the collection of Devanagari fonts available to designers, publishers, and users worldwide. Its open-source nature and high-quality design make it a popular choice for projects that require a modern and accessible Devanagari typeface.
by Prof. Girish Dalvi
by Prof. Anirudha Joshi and Team Swarachakra
by National Payments Corporation of India (NPCI)
by Manish Khera & Rishi Gupta
by National Informatics Centre under the Ministry of Electronics and Information Technology (MeitY)
by AssisTech, IIT Delhi
by Abhiraj Bhal, Varun Khaitan & Raghav Chandra
by Government of India
by Prathap Bhimasena Rao
by IIT Madras
by Tactopus Team
by National Council of Educational Research and Training (NCERT)
by IIIT Bangalore
by Ministry of Health & Family Welfare, Government of India
by Shubhranshu Choudhary
by Ministry of Rural Development, Government of India
2020-2024
(1 items)
by Zoho Corporation
2021-2024
(3 items)
by Government of India
by Government of India
by Government of India